uv reactors, photo-oxidation, advanced oxidation (aop), recycling & engineering
for industrial use
Direct Photolysis
Along with initiating reactions via OH radicals (generated from H2O2) the direct photolysis of water ingredients by UV irradiation plays a major part. However, sufficient absorption of these substances is required, which can then selectively be destroyed under proper process conditions. Especially the possibility of a selective oxidation of toxic ingredients is a major advantage with respect to costs and efficiency.


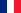





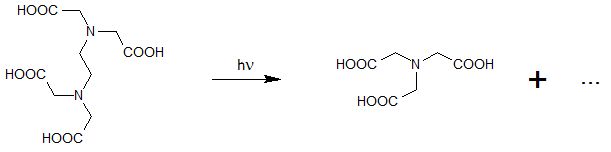
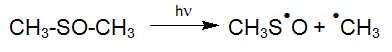
![[Translate to EN:] NDMA (N-Nitrosodimethylamin)](https://www.enviolet.com/fileadmin/DAM/enviolet/UV-Oxidation/Direkte%20Fotolyse/NDMA.png)